What is Familiar
Familiar is a cross-platform Family Tree (Genealogy) software. It has been tested on Linux and Windows. Family tree manipulation/management fully supports drag and drop. Further multiple types of views are supported. Importing and exporting to GedCom format is supported, allowing sharing data across different applications.
Features
· Fully functional drag and drop support. Multiple views let you see the data as you want to see it.
· Custom events enhance the way you want to store/see data. There is no limitation on what and how many events you can have.
· Built in rich text support for giving rich description to your events and/or to give notes on individuals. There is rich text editor which lets you edit rich text directly.
Getting Started
 First, Some Definitions
First, Some Definitions
1.
Family: A Family Tree can have as
many Families as one wants. A Family is starting point of the Family Tree. A
Family can have any number of Individuals as Primary Members. Families
can be of two types: base and non-base. Base families are
displayed at the top of the tree, while non-base families are displayed after
base families. If there are more than one base (or non-base) families, they are
sorted before displaying. A family is represented by ![]() in a family tree.
in a family tree.
2.
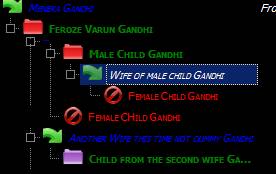
Primary Member:
Primary Member is any Individual who is at the top of his/her family
tree, i.e. he/she is direct child node of a family. There can be any number of
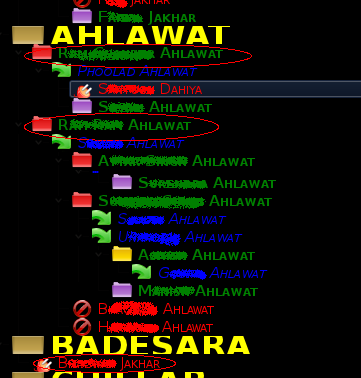
Primary Members in a Family. For example, All items marked with circle in Fig 1
are primary members. The Ahlawat family has two primary members.
3.
Individual:
An Individual is the basic unit in Familiar. Sex of an Individual can be either
male or female. An Individual can be in Union with another Individual
(of opposite sex). A female individual, who has been married, will be shown multiple
times in the family tree. For example, if a female Individual has married
twice, she will be shown three times – once in the role of daughter, and twice
in the role of wife. An individual may be represented in the following way
(depending upon his type and role):
|
Type/Role |
Icon |
|
Unmarried Male |
|
|
Married Male without children |
|
|
Married Male with children |
|
|
Unmarried female |
|
|
Married female represented as daghter |
|
|
Married female represented as wife |
|
4. Event: An Event is an event that occurred during the life time (or even otherwise) of one or more Individuals. Events can be shared by multiple Individuals. There can be any number of events of any type. Four basic types of events are currently supported, viz. Birth, Death, Marriage, and Divorce. Other types of events can be created as deemed necessary. Events contain information such as Date, Place, and Description.
Different type of
views: There are multiple views that are supported in the various tabs in
Familiar. You just need to select the appropriate tab to enable these views. Tip:
In all views you can hover over individuals/families to get a preview of their
details.
1.
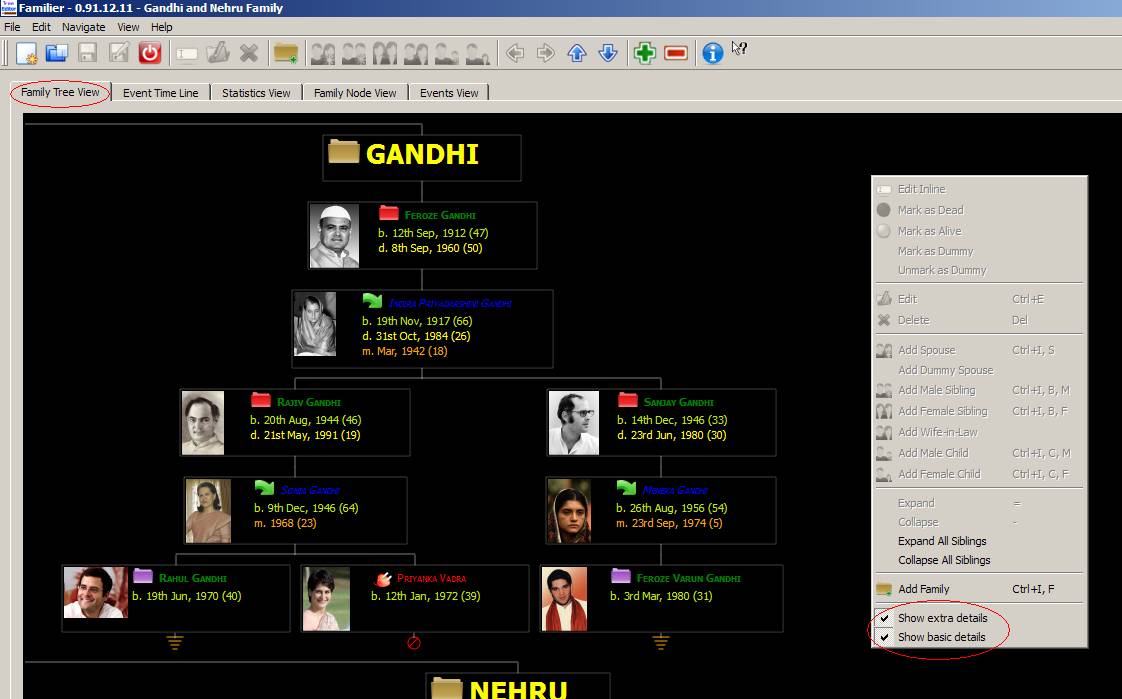
Family Tree View: In this view family tree can be
seen. It supports three types of views, which are given below.
A.
No Details View:
To make the current view No Details View, right click and deselect the Basic Details View and the Extra Details View.
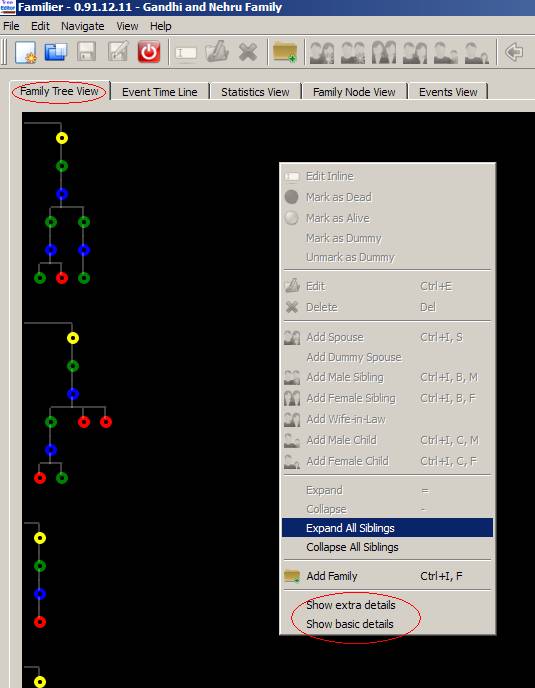
B.
Basic Details View: To make the current view Basic Details View, right click and
select the Basic Details View and
deselect the Extra Details View.
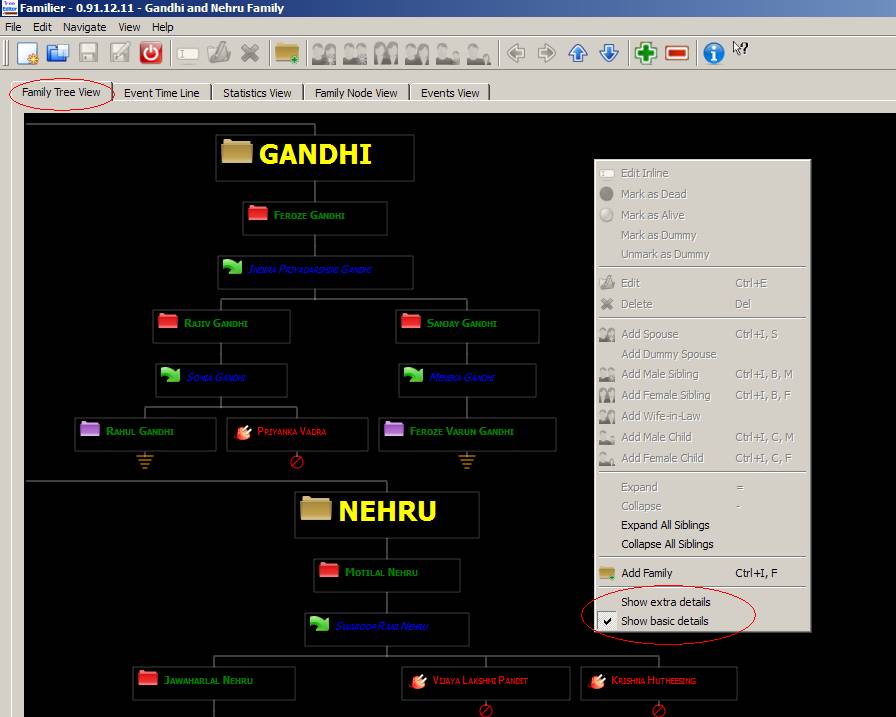
C.
Extra Details View: To make the current view Extra Details View, right click and
select the Basic Details View and the
Extra
Details View.
2.
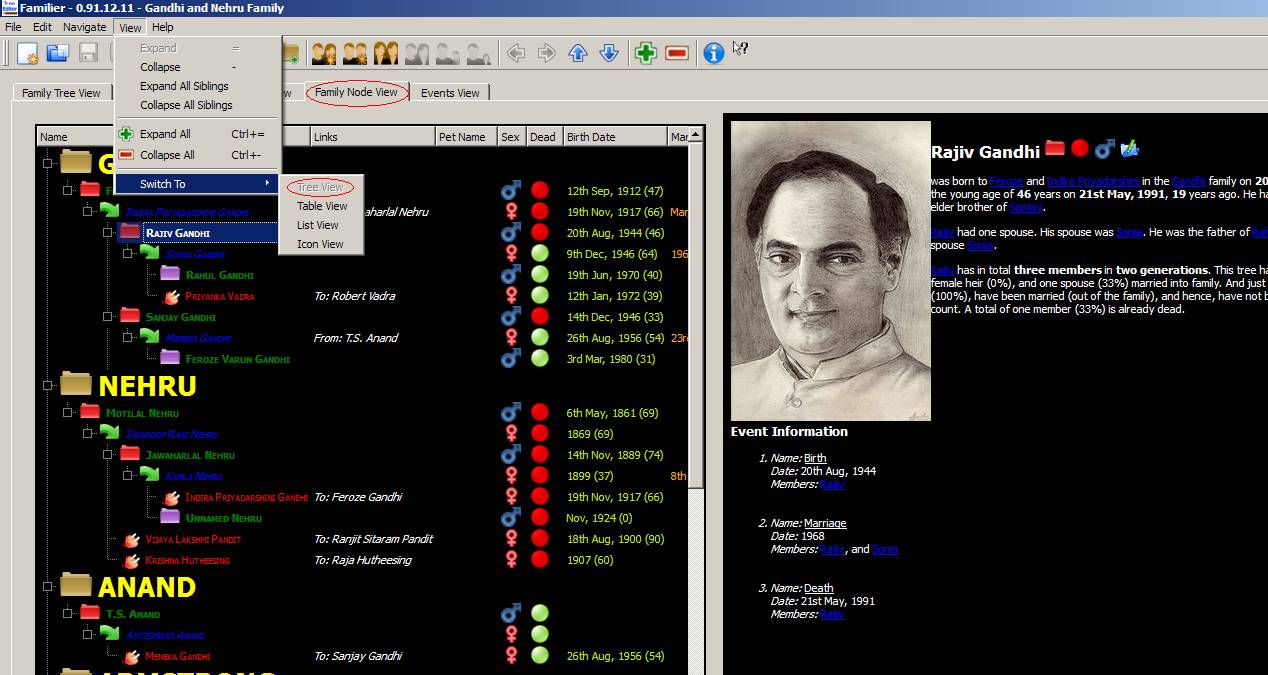
Family Node View: To select this
click on Family Node View. Four
different types of views are supported by this view, as given below.
A.
Tree View
B.
Table View
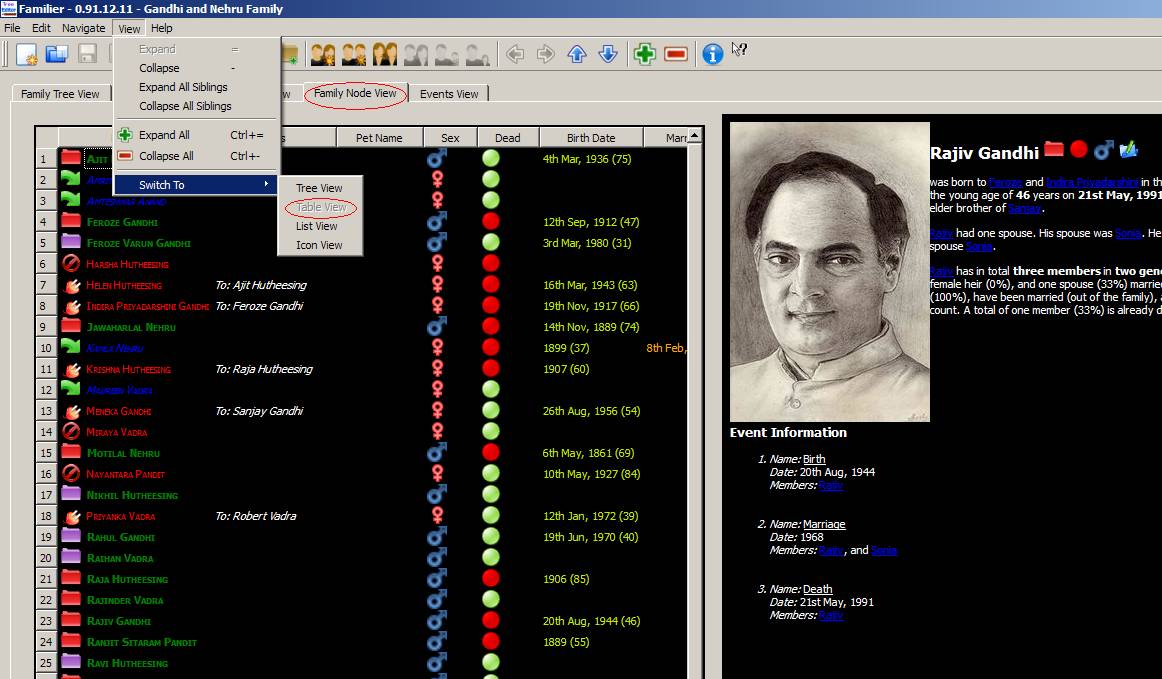
C.
List View
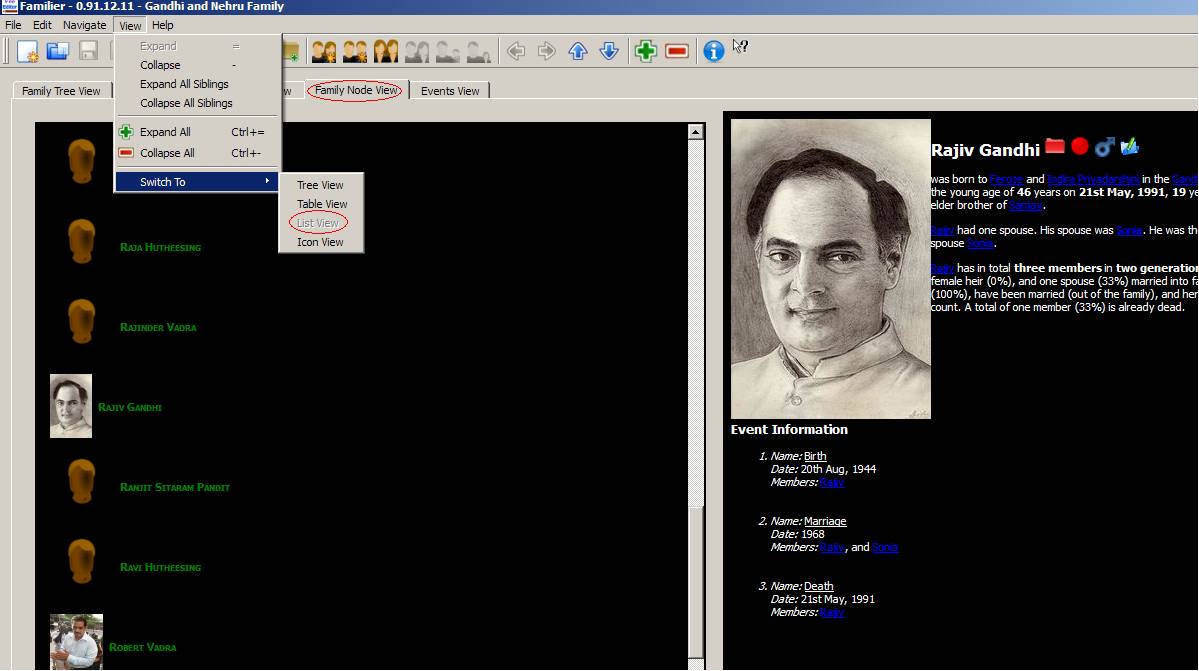
D.
Icon View
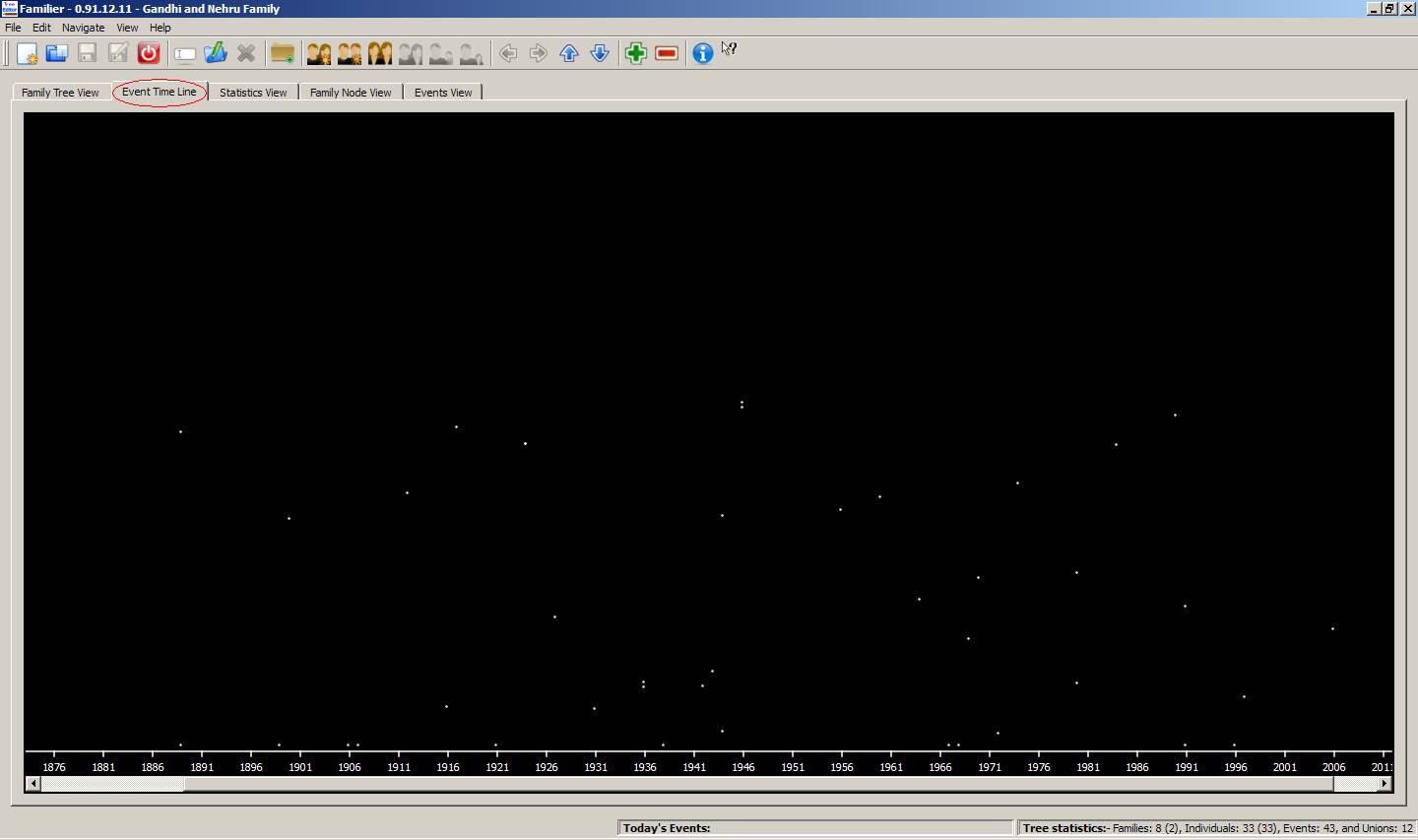
3.
Event
Time Line: This view is for displaying
events time line. Each dot represents an event.
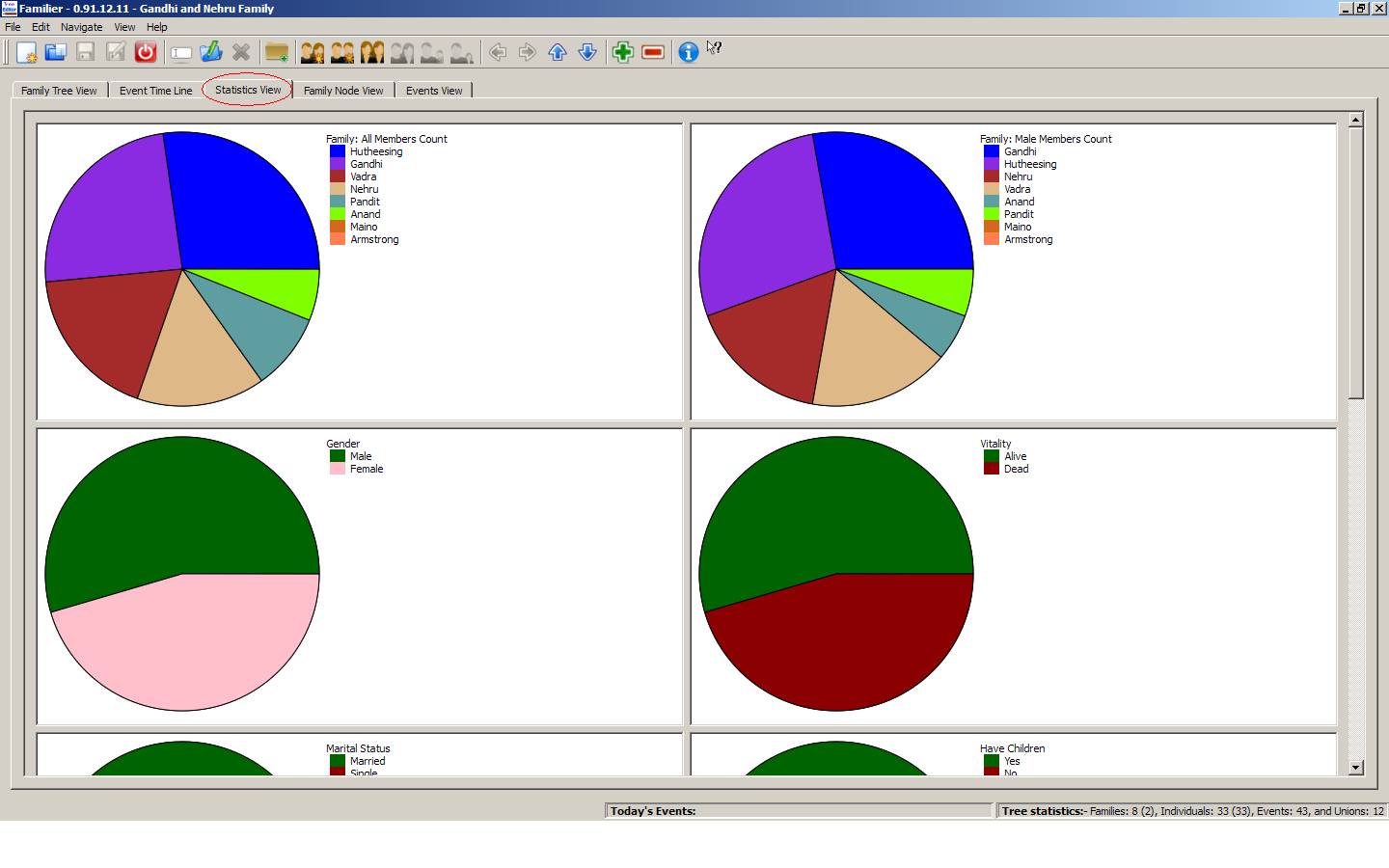
4.
Statistics
View
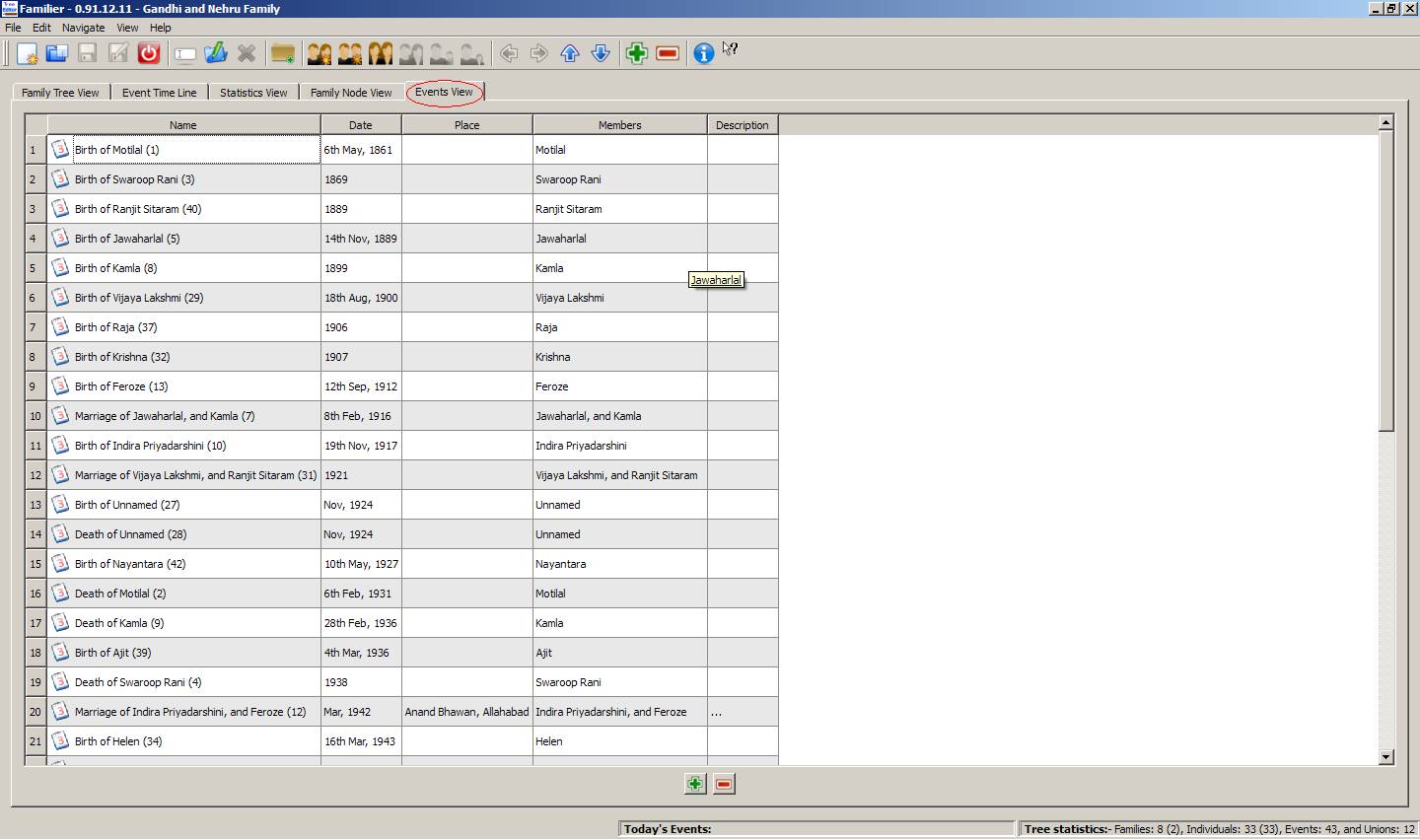
5.
Events
View
3.
Creating a Family Tree: Family Tree
can be created/modified either in Family
Tree View or in Family Node View,
or any of their child views.
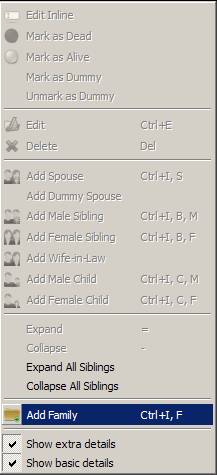
1.
Adding Family: Family can be added as apparent from the screenshot below. Any number of
families can be added to a Family Tree. Essentially, all members of a Family
share the same Last Name. A Family can have multiple Primary Members.
2.
Adding Individuals: An Individual can be added either to a family (as Primary Member) or to
another Individual. The following table explains
Parent Type
|
Can
Add
|
||||||
|
|
Spouse
|
Dummy Spouse
|
Male Sibling
|
Female Sibling
|
Wife-in-law
|
Male Child
|
Female Child
|
Family
|
No
|
No
|
No
|
No
|
No
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Male Individual
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
No
|
No
|
Female Individual
in the role of Wife
|
No
|
No
|
No
|
No
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Female Individual
in the role of Daughter
|
No
|
No
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
No
|
No
|
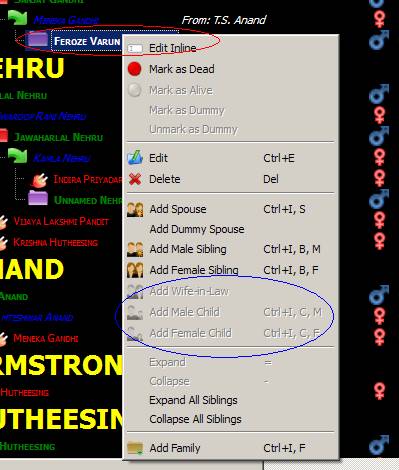
3. Adding Child to a Male Individual: One cannot add a child to a male individual. A child can be added to a
female Individual in the role of wife only. As can be seen from the screenshots
below.
Individual marked in the red is unmarried male. As a result he cannot have
children directly.
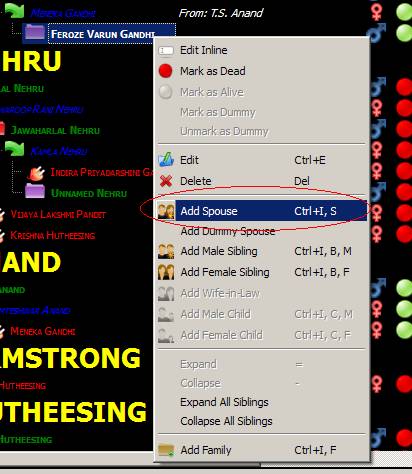
Next we add a spouse (A Dummy Spouse can be added just as well).
If we right click the spouse we
can now add children, as well as a wife-in-law.
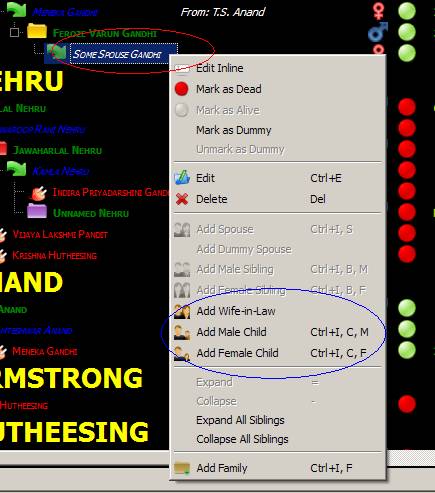
4. Dummy Spouse: Dummy spouse
is a Female Individual in the role of wife, about whom we do not have much
idea. In Familiar, only Female Individuals in the role of wives can have
Children. As a result, one should create dummy spouses to add children to Male
Individuals whose spouses are unknown. These are visible as tiny dots in Family Node View. Please refer to
screenshots below:
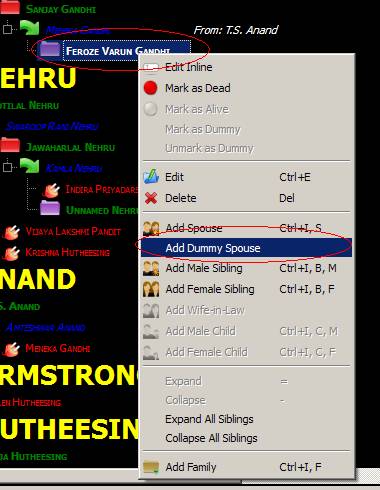
We are adding a dummy Spouse in
the screenshot above, because we cannot add children to this Individual
otherwise.
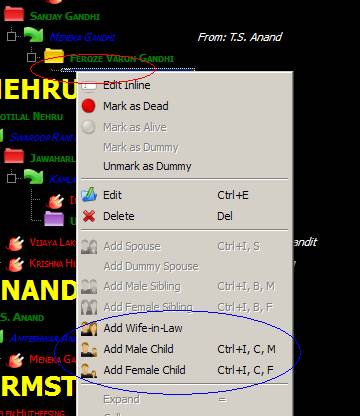
The dummy spouse is marked with
red circle in the screenshot above. Note, we can now add children and other
spouse (Add Wife-in-Law).
Now we can construct the whole
tree for this Individual. Note also, other wives can be dummy or not.
5. Adding Individuals to a
Family
Both male and
female individuals can be added to a family. These are also called Primary
Members. A Male Primary Member can have spouses (female). On the other hand,
female Primary Members cannot have any children or spouses (as they are Females
in role of daughter).
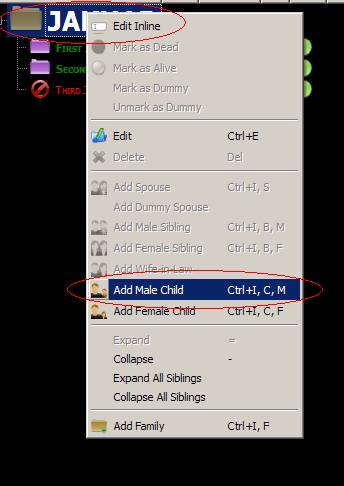
6. Adding child as opposed to
adding sibling
Adding as child
adds as first child, as can be seen:
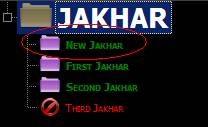
Adding as
sibling adds as next child, as can be seen below:
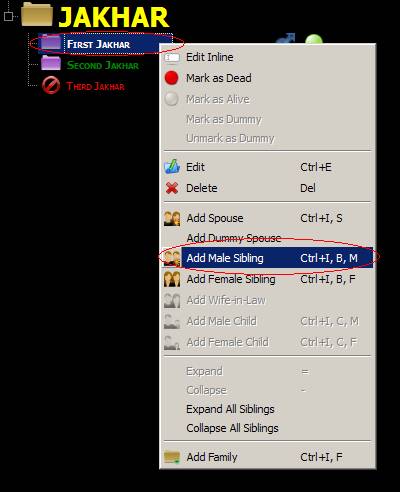

Another example,
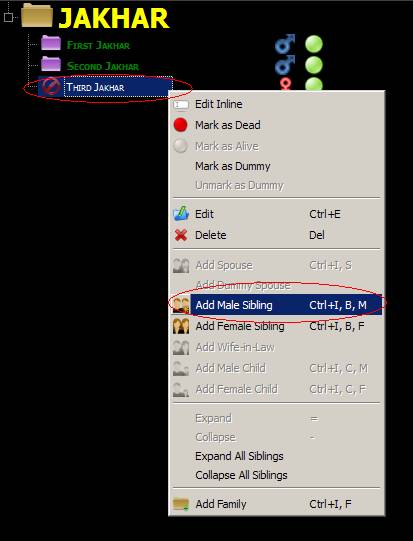

So to summarize Add Male Sibling, Add Female Sibling, and Add Wife-in-law behave as Sibling in the
examples above, while Add Spouse, Add Dummy Spouse, Add Male Child, and Add
Female Child, behave as Child in the examples above, no matter from where
you click on them.
7.
The Drag/Drop functionality: An Individual can be dragged and
dropped to another Individual or Family. The following menu appears, when you
drop an Individual onto another Individual or Family:
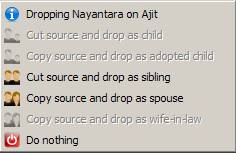
Certain menu entries will appear grayed out, depending on source and
destination. Cut means that original individual will disappear from source and
appear on destination. Copy means that source remains while the same individual
will appear on destination. Note no matter how many times an individual is copied the underlying data is
shared. So even though the individual is visible at multiple locations on the
Family Tree, it is one and the same individual.
Depending on what you are dropping on whom the following possibilities exist:
A.
Cut
source and drop as child
B.
Copy
source and drop as adopted child
C.
Cut
source and drop as sibling
D.
Copy
source and drop as spouse
E.
Copy
source and drop as wife-in-law
The following table summarizes all
the possible source and destination combinations. The letter codes are as
listed above.
Source →
|
Family
|
Male
|
Female (as daughter)
|
Female (as spouse)
|
Family
|
Never
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
Male
|
Never
|
C
|
C, and D
|
C, and D
|
Female (as daughter)
|
Never
|
C
|
C
|
C
|
Female (as spouse)
|
Never
|
A, and B
|
A, B, and E
|
A, B, and E
|